Systemd is the default init system for most modern Linux distributions, including Ubuntu, CentOS, Fedora, and Debian. It plays a crucial role in managing system services and processes. To harness the power of systemd, you need to become familiar with the systemctl command. In this blog post, we'll explore essential systemctl commands to manage a service running on a Linux system.
What is systemctl?
systemctl is a command-line tool for controlling the systemd system and service manager. It allows you to manage system services, inspect their status, start, stop, enable, or disable them, among other things. This tool simplifies sysadmin tasks, making it easier to maintain a healthy Linux system.
How to List All Enabled and Disabled Services
To get an overview of all services on your system, both enabled and disabled, you can use the following command:
systemctl list-unit-files -at serviceOutput:
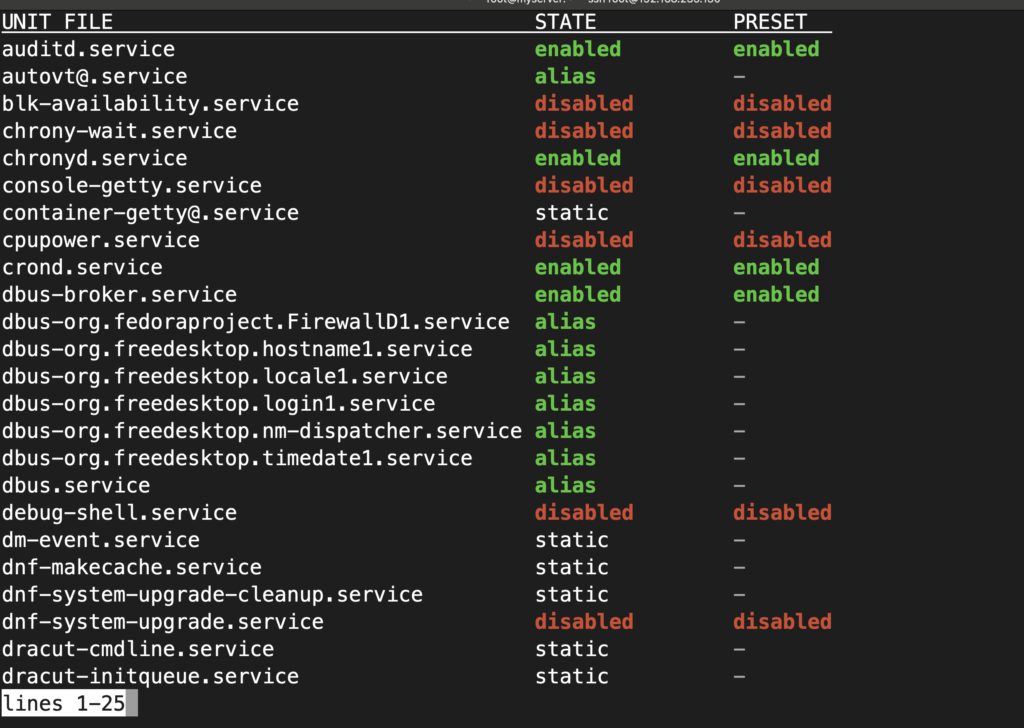
This command provides a comprehensive list of services, their statuses, and whether they are set to start automatically during boot.
How to List All Services and Their Statuses
To see a detailed list of all services and their current statuses, including active, inactive, and failed services, use the following command:
systemctl list-units -at serviceOutput:

This command gives you a real-time snapshot of the status of all services on your system.
How to List Running Services
If you want to view only the services that are currently running, you can filter the list using this command:
systemctl list-units -at service --state=runningOutput:

This is particularly useful when you need to identify which services are actively using system resources.
How to Display the Content of a Service File
To examine the content of a service file, such as the configuration for the rsyslog service, use the systemctl cat command:
systemctl cat rsyslogThis command displays the contents of the service file, making it easier to understand its configuration.
How to Check the Status of a Service
To check the current status of a specific service, use the systemctl status command, followed by the service name, like this:
systemctl status sshd.serviceThis command provides detailed information about the service's state, including whether it's active, running, and enabled. It also shows recent log entries.
Output:

How to Start, Stop, Reload and Restart Services
Managing services is a fundamental part of system administration. Use these commands to start, stop, or restart a service, such as httpd.
To start a service e.g httpd:
systemctl start httpdTo stop a service:
systemctl stop httpdTo reload a service:
systemctl reload httpdTo restart a service:
systemctl restart httpdReloading a service is always a good idea over restarting it if you are modifying a configuration and want to reload. Restarting the service can cause downtime as it will first stop the service and start it back.
How to Check if a Service is Active
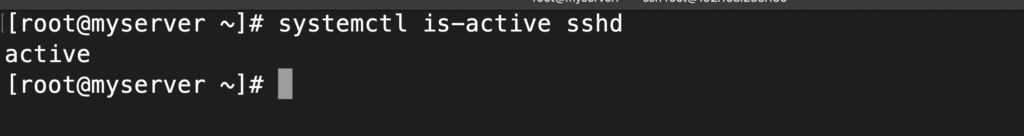
To quickly check whether a service is currently active, you can use the systemctl is-active command, followed by the service name. For example:
systemctl is-active sshdOutput:
How to Enable, Disable, Mask, and Unmask Services
Enabling a service ensures that it starts automatically during system boot. Conversely, disabling a service prevents it from starting automatically. You can use these commands.
To enable a service:
systemctl enable auditdTo disable a service:
systemctl disable auditdSometimes, you may want to mask a service, which effectively prevents it from being started by any means. To mask a service:
systemctl mask auditdTo unmask a previously masked service:
systemctl unmask auditdHow to Check if a Service is Enabled
To verify whether a service is enabled to start automatically at boot, use the following command:
systemctl is-enabled auditdThis command will return enabled if the service is set to start during boot.
Conclusion
Learning systemctl commands are essential for managing and maintaining Linux systems. These commands help you to control services, troubleshoot issues, and keep your system running smoothly. In this blog post, we covered all the essential systemctl commands you need to know in order to properly manage services in a Linux system.






